What Is JavaScript
![]()
JavaScript, often abbreviated as JS, is a programming language and core technology of the Web, alongside HTML and CSS. 99% of websites use JavaScript on the client side for webpage behavior
Web browsers have a dedicated JavaScript engine that executes the client code. These engines are also utilized in some servers and a variety of apps. The most popular runtime system for non-browser usage is Node.js.
JavaScript is a high-level, often just-in-time compiled language that conforms to the ECMAScript standard. It has dynamic typing, prototype-based object-orientation, and first-class functions. It is multi-paradigm, supporting event-driven, functional, and imperative programming styles. It has application programming interfaces (APIs) for working with text, dates, regular expressions, standard data structures, and the Document Object Model (DOM).
The ECMAScript standard does not include any input/output (I/O), such as networking, storage, or graphics facilities. In practice, the web browser or other runtime system provides JavaScript APIs for I/O.
Although Java and JavaScript are similar in name, syntax, and respective standard libraries, the two languages are distinct and differ greatly in design.
JavaScript
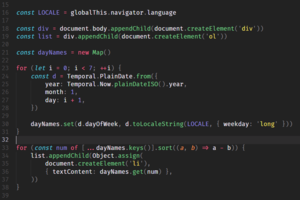 |
| Screenshot of JavaScript source code |
| Paradigm | Multi-paradigm: event-driven, functional, imperative, procedural, object-oriented |
|---|---|
| Designed by | Brendan Eich of Netscape initially; others have also contributed to the ECMAScript standard |
| First appeared | December 4, 1995 |
| Stable release | |
| Preview release | ECMAScript 2025
/ 27 March 2024 |
| Typing discipline | Dynamic, weak, duck |
| Filename extensions |
|


Post a Comment